SYSTEMS/GLASS AND METAL CURTAIN WALLS
Mullion Design
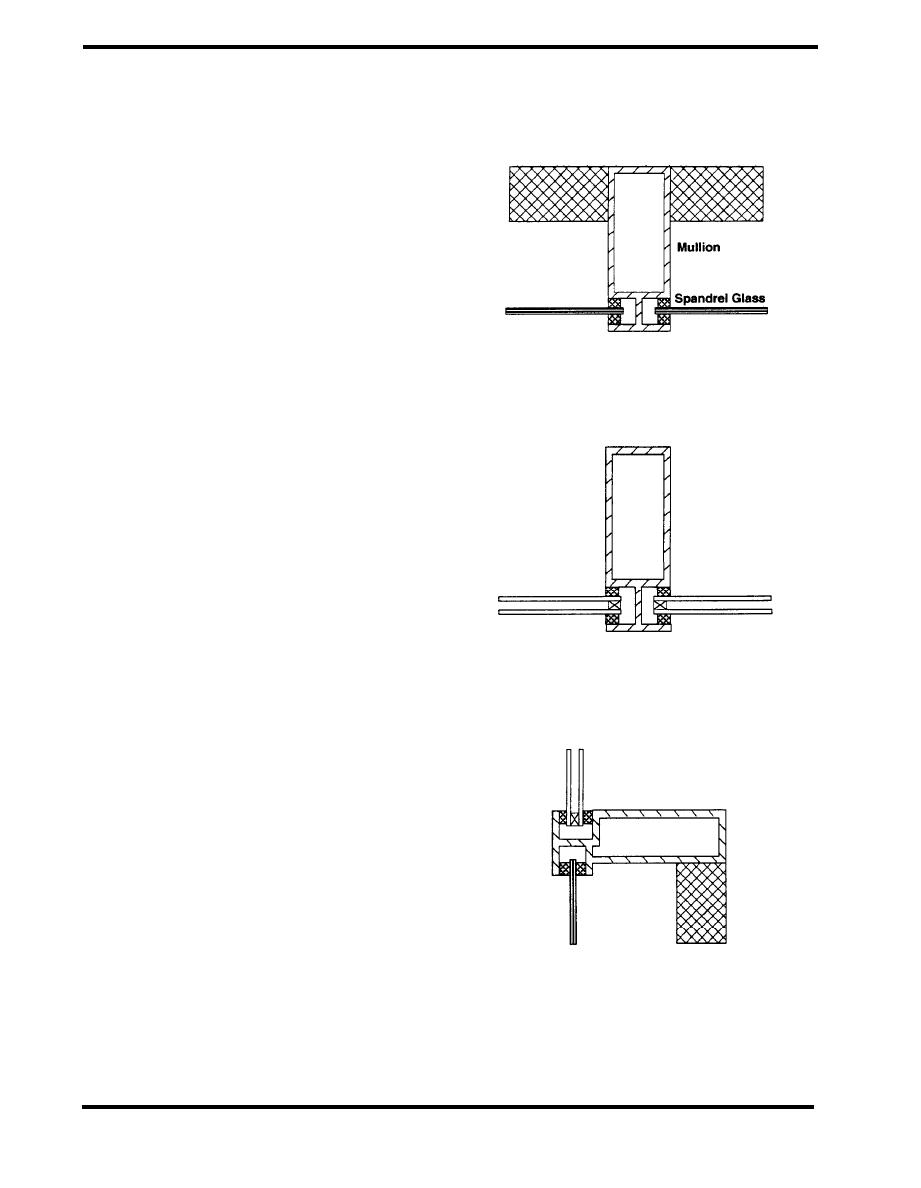
UNACCEPTABLE
Insulation
The design of curtain wall mullions is crucial in
achieving air barrier and insulation system
continuity. Figure 4.1.1 showed a generic
representation of a thermally broken mullion.
Effective mullion designs must include thermal
breaks and a means of pressure equalization
and drainage. Pressure equalization removes
the wind forces that would otherwise force water
through the outer seal, protecting the inner air
seal from deterioration due to exposure to
Vertical Mullion at Insulated Glass Spandrel
water. Weepholes provide for the drainage of
water that does penetrate the pressure
equalization cavity and must be shielded against
UNACCEPTABLE
the penetration of wind-driven rain. The AAMA
Window Selection Guide contains a detailed
discussion of mullion and window frame design,
with numerous examples of mullion designs.
Figure 4.1.2 shows generic, thermally-unbroken
mullion designs for three different applications: a
vertical mullion at an insulated glass spandrel, a
Vision Glass
vertical mullion at vision glass and a horizontal
mullion at the intersection of vision glass with a
glass spandrel. All of these systems suffer from
the same basic problem, thermal bridging at the
Vertical Mullion at Vision Glass
aluminum web connecting the main mullion
section to the exposed surface of the mullion.
This thermal bridging results in increased heat
loss through the mullion, as well as an increased
UNACCEPTABLE
potential for condensation on interior surfaces
under heating conditions. Airtightness is related
to the air seal materials used and their ability to
accommodate differential movement at this
location.
Horizontal Mullion at Vision/Spandrel Interface
Figure 4.1.2 Thermally Unbroken Mullions
PAGE 4.1-2



 Previous Page
Previous Page
