Section 2: Individual LEED Credit Reviews
LEED Credit EQ-4.4:
Millwork substrate boards must be specified
to ensure that urea-formaldehyde binders are
Low-Emitting Materials
excluded. Acceptable options include:
Composite Wood
◦ Mdf using an MDI binder
◦ Plywood using a phenol-formaldehyde
binder (typically sanded, exterior grade
Intent
softwood panels)
◦ Particleboard using a phenol-formaldehyde
Reduce the quantity of indoor air contaminates
binder
that are odorous, potentially irritating and/or
◦ Straw-based particleboard/mdf using an
harmful to the comfort and well-being of
MDI binder
installers and occupants.
◦ All solid wood components
Requirement
Wood doors must be specified to ensure that
any composite wood or agrifiber material
Composite wood or agrifiber products must
included in the door assembly does not
contain no added urea-formaldehyde resins.
contain urea-formaldehyde binders.
(1 point)
Acceptable options include:
◦ For rails and stiles: Solid wood, or
Cost Impact = 4 or 5
laminated strand lumber (LSL) that uses an
MDI binder
◦ For solid cores: Solid wood (stave core),
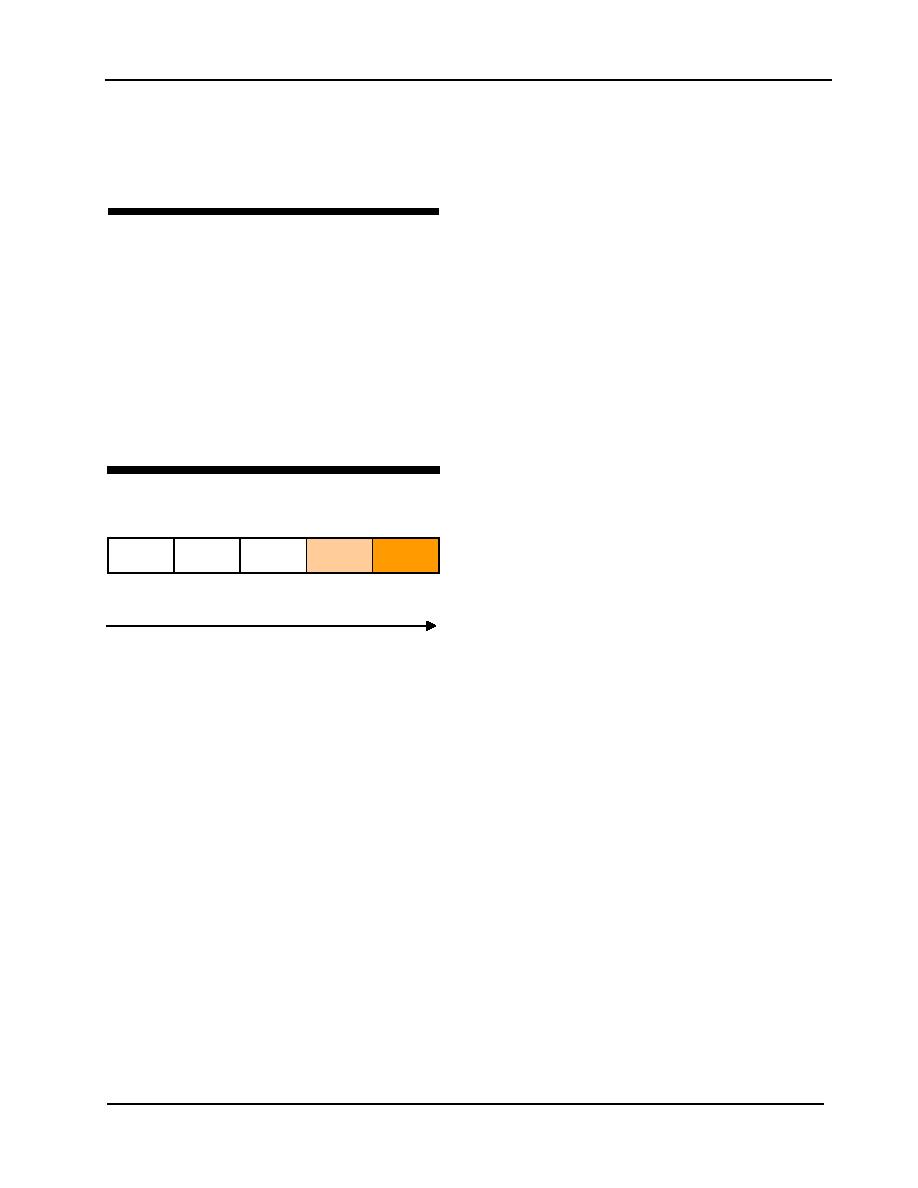
1
2
3
4
5
particleboard that uses a phenol-
formaldehyde binder, mdf that uses an
GSA
No
Low
Moderate
High
MDI binder, or LSL that uses an MDI
Standard
premium,
premium
premium
premium
binder
(no cost)
psble svgs
(<50K)
(50-150K)
(>150K)
◦ Cross-banding layers: Hardboard that does
not contain urea formaldehyde
Practical Applications
Miscellaneous blocking or mounting panels
Urea formaldehyde is commonly used in composite
must be specified to ensure that urea-
wood products such as hardwood plywood,
formaldehyde binders are excluded.
particleboard, and medium density fiberboard
Acceptable options include:
(mdf). In commercial buildings, these board
products are typically used as substrates for
◦ Plywood using a phenol-formaldehyde
cabinetry, paneling and other millwork items, as
binder (typically exterior grade softwood
miscellaneous blocking or mounting panels, and as
panels)
cores or stabilizing layers in wood doors.
◦ Other options noted under the millwork
Composite wood and agrifiber boards are also used
section above
in many furniture items; however, moveable
furniture is not included in the scope of this LEED
Basis for Cost Assumption
credit. Acceptable binders for composite wood and
agrifiber products include phenol-formaldehyde
The study assumes that none of the urea
and MDI (methyl diisocyanate), a polyurethane-
formaldehyde-free composite wood and agrifiber
based binder.
products listed above are typical for GSA projects,
with the exception of the softwood plywood panels
To earn this LEED credit, projects will likely need
used for blocking or mounting panels. In all other
to implement the following measures:
applications, it is assumed that urea-formaldehyde-
free products are substituted for more traditional
GSA LEED COST STUDY
143



 Previous Page
Previous Page
