PRINCIPLES/DEFECTS
Thermal Bridges
.
Structural elements
.
Component connections
.
Envelope penetrations
.
Corner effects
Thermal bridges are relatively high conductivity building elements that penetrate the envelope
insulation, thereby leading to increased heat flow rates. The literature contains much discussion of
thermal bridges, and Tye has divided them into four categories, structural elements, component
connections, envelope penetrations and corner effects.
Structural elements are high strength and relatively high conductivity elements used to connect
building elements to the building structure that act as thermal bridges when they penetrate the
envelope insulation system. Bridges of this type include large elements such as beams, floor slabs,
insulation fasteners.
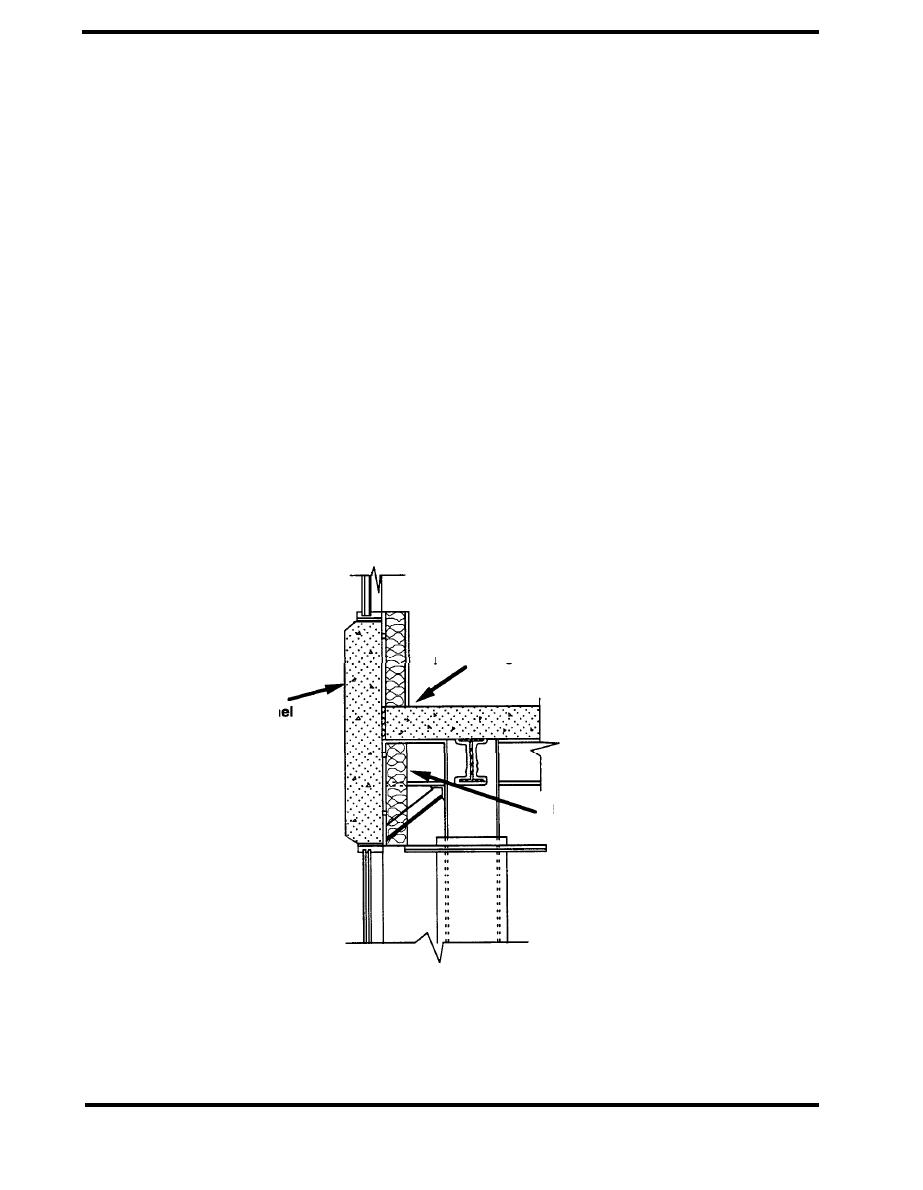
The penetration of the insulation system by floor slabs is a very common thermal bridge, occurring
in many envelope designs as well as many construction handbooks. Figure 2.3.1 shows such a
thermal bridge associated with a floor slab and an outrigger beam supporting a precast concrete
panel (Childs). Both the floor slab and the beam penetrate the exterior wall insulation, increasing
the heat transmission rate by a factor of two in the region of the thermal bridge.
UNACCEPTABLE
Floor slab
penetrating insulation
Precast
concrete pan
Beam and panel support
penetrating insulation
Figure 2.3.1 Beam and Floor Slab Penetrating Insulation (Childs)
PAGE 2.3-2



 Previous Page
Previous Page
